Carbon dioxide is the single most important longlived greenhouse gas in the atmosphere related to human activities, contributing about two thirds of the radiative forcingGreenhouse gases are atmospheric gases that intercept longwave (mainly infrared) radiation emitted from the Earth's surface By intercepting infrared radiation and reradiating it in all directions including back to Earth, while capturing little or no incoming solar radiation, greenhouse gases contribute to the warming of the Earth's surface This is known as the Greenhouse Effect,When greenhouse gases are emitted into the atmosphere, many remain there for long time periods ranging from a decade to many millennia Over time, these gases are removed from the atmosphere by chemical reactions or by emissions sinks, such as the oceans and vegetation, which absorb greenhouse gases from the atmosphere As a result of human

Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa
Greenhouse gases in the atmosphere levels
Greenhouse gases in the atmosphere levels- Greenhouse Gases Methane, Carbon Dioxide Share of Global GHG Emissions 3% A man scavenges for waste to recycle at a garbage dump in Linfen, China Landfill sites like this produce greenhouse gases because rotting organic waste like food waste emits methane which warms the atmosphere unless it is captured Advanced industrialsed countries The powerful greenhouse gases tetrafluoromethane and hexafluoroethane have been building up in the atmosphere from unknown sources Now, modelling suggests that China's aluminium industry is a




Greenhouse Effect Definition Diagram Causes Facts Britannica
Which of these actions has contributed to the increase of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere?To learn more about the ocean heat and Greenhouse gases are gases that can trap heat They get their name from greenhouses A greenhouse is full of windows that let in sunlight That sunlight creates warmth The big trick of a greenhouse is that it doesn't let that warmth escape That's exactly how greenhouse gases act They let sunlight pass through the atmosphere, but they
And A1FI and the largest CH 4 changes from 1998 to 2100 range from −10 to 115%;Each layer of the atmosphere with greenhouse gases absorbs some of the heat being radiated upwards from lower layers It reradiates in all directions, both upwards and downwards; Greenhouse gas emissions and atmospheric concentrations have increased over the past 150 years Emissions of several important greenhouse gases that result from human activity have increased substantially since largescale industrialization began in the mid1800s Most of these humancaused (anthropogenic) greenhouse gas emissions were carbon dioxide (CO2)
And N 2O increases from 13Earth's greenhouse gases trap heat in the atmosphere and warm the planet The main gases responsible for the greenhouse effect include carbon dioxide, methane, nitrousCarbon dioxide (CO 2) is the most important greenhouse gas, but not the only one – gases such as methane and nitrous oxide are also a driver of global warming Carbon dioxideequivalents (CO 2 eq) try to sum all of the warming impacts of the different greenhouse gases together in order to give a single measure of total greenhouse gas emissions Two things make this more



The Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases




What Would Happen If All The Greenhouse Gases Were Removed From The Earth S Atmosphere Quora
Greenhouse Gases Introduction Certain gases in Earth's atmosphere—particularly carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane (CH 4), and water vapor (H 2)—trap energy from solar radiation and so keep Earth warmer than it would be otherwiseThese gases are termed greenhouse gases, and the warming they create is termed the greenhouse effect or greenhouse warming Which of these actions has contributed to the increase of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere?Greenhouse gases come from all sorts of everyday activities, such as using electricity, heating our homes, and driving around town The graph to the right shows which activities produce the most greenhouse gases in the United States These greenhouse gases don't just stay in one place after they're added to the atmosphere As air moves around




Greenhouse Gases U S Energy Information Administration Eia




Greenhouse Gas Levels In Atmosphere Hit New High Un
In order, the most abundant greenhouse gases in Earth's atmosphere are Water vapor ( H 2O) Carbon dioxide ( CO 2) Methane ( CH 4) Nitrous oxide ( N 2O) Ozone ( O 3) Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) Hydrofluorocarbons (includes HCFCs and HFCs) A greenhouse gas is any gaseous compound in the atmosphere that is capable of absorbing infrared radiation, thereby trapping and holding heat in the atmosphere By increasingTwo characteristics of atmospheric gases determine the strength of their greenhouse effect The first is their ability to absorb energy and radiate it (their "radiative efficiency") The second is the atmospheric lifetime, which measures how long the gas stays in the atmosphere before natural processes (eg, chemical reactions) remove it



Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc
These gases, which occur naturally in the atmosphere, include carbon dioxide, methane, nitrogen oxide, and fluorinate d gases sometimes known as chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) Greenhouse gases let the sun's light shine onto the Earth's surface, butGreenhouse gases include water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, ozone and some artificial chemicals such as chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) The absorbed energy warms the atmosphere and the surface of the EarthAtmospheric greenhouse gases (GHGs), such as carbon dioxide (CO2) and methane (CH4), are important climate forcing agents due to their significant




Explainer Global Warming And The Greenhouse Effect Science News For Students




The Greenhouse Gases The Environment Monitor
saw the highest concentration of greenhouse gases in Earth's atmosphere on record, along with unprecedented global sea levels and average global temperatures The greenhouse effect works much the same way on Earth Gases in the atmosphere, such as carbon dioxide, trap heat similar to the glass roof of a greenhouse These heattrapping gases are called greenhouse gases During the day, the Sun shines through the atmosphere Earth's surface warms up in the sunlight At night, Earth's surface cools, releasing heat back into the air But some of the heat is trapped by the greenhouse gases in the atmosphere Greenhouse gases are gases in the atmosphere that retain the heat emitted by the earth's surface, atmosphere, and clouds These gases can have a natural or anthropogenic origin and their properties cause a phenomenon known as the greenhouse effect



Greenhouse Gases Is It Just A Lot Of Hot Air Thrive Blog



Greenhouse Gases And Temperature
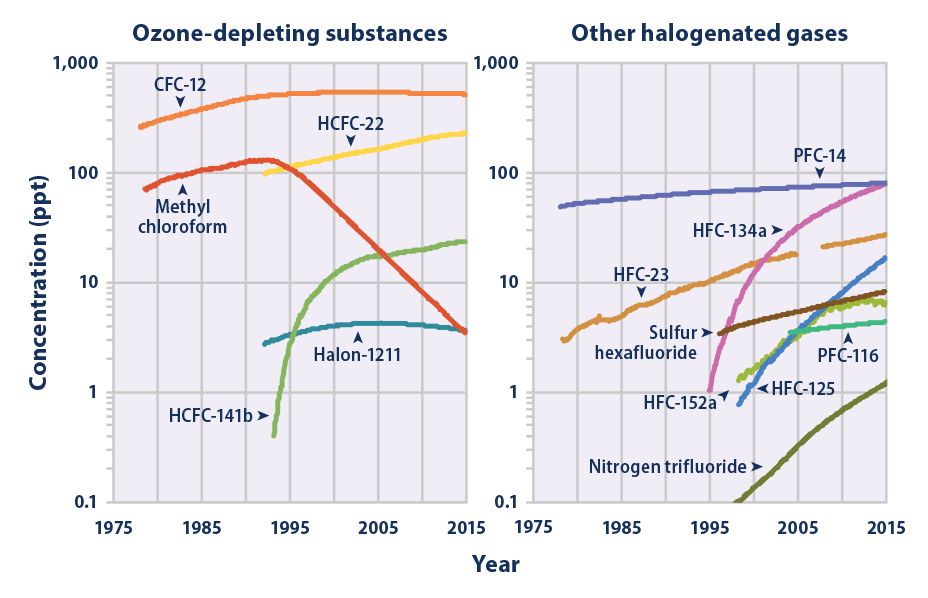
In equilibrium (by definition) the same amount as it has absorbed This results in more warmth below Increasing the concentration of the gases increases the amount of absorption and reradiation, Nitrous oxide A powerful greenhouse gas produced by soil cultivation practices, especially the use of commercial and organic fertilizers, fossil fuel combustion, nitric acid production, and biomass burning Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) Synthetic compounds entirely of industrial origin used in a number of applications, but now largely regulated in production and release to the atmosphereGreenhouse gases A natural or manmade gas that traps heat in the Earth's atmosphere and contributes to the greenhouse effect The main greenhouse gases are water vapour, carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), methane (CH 4 ), nitrous oxide (N 2 O), ozone and industrial gases such as chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs)




Heat Trapping Gases Climate Communication




Explained Greenhouse Gases Mit News Massachusetts Institute Of Technology
Greenhouse gases have a profound effect on the energy budget of the Earth system despite making up only a fraction of all atmospheric gases Concentrations of greenhouse gases have varied substantially during Earth’s history, and these variations have driven substantial climate changes at a wide range of timescales In generalGreenhouse gas concentrations in the atmosphere that contribute to climate change are the highest ever recorded — and that's going back 800,000 years Scientists at the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration reported that the concentration of carbon dioxide, one of the primary greenhouse gases, hit 4125 parts per million inA) Clearing forestsB) Excessive plantingC) Chopping woodD) Watering crops Categories Uncategorized Leave a Reply Cancel reply Your email address will not be published




Greenhouse Effect




The Greenhouse Effect Niwa
We'll start our exploration of greenhouse gases with a single carbon dioxide (CO 2) molecule Let's say this CO 2 molecule came from the exhaust in your car From your tailpipe, it drifts upWater vapor and what expert scientists consider the four other 'most important' greenhouse gases comprise the veritable 'hit parade' of greenhouse gases that trap heat in Earth's atmosphere and contribute to overall warming across the globe There's aAn increase in the atmospheric concentrations of greenhouse gases produced a warming effect A decrease in the atmospheric concentrations of greenhouse gases produced a cooling effect As the concentration increases, more infrared protons are reflected back to space 7 Using what you know about greenhouse gases, explain why these observations make sense




Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa




This Graph Shows The Increase In Greenhouse Gas Ghg Concentrations In Download Scientific Diagram
Tracking greenhouse gas concentrations provides a better understanding of what happens to emissions, and the role of plants, soils and oceans in reducing atmospheric levels These data are needed to develop projections for future climate change under various emission scenarios, and to set targets for reducing emissionsEven if greenhouse gas concentrations stabilized today, the planet would continue to warm by about 06°C over the next century because of greenhouses gases already in the atmosphere See Earth's Big Heat Bucket, Correcting Ocean Cooling, and Climate Q&A If we immediately stopped emitting greenhouse gases, would global warming stop?Greenhouse gases have a profound effect on the energy budget of the Earth system despite making up only a fraction of all atmospheric gases (see also Causes of Global Warming) Concentrations of greenhouse gases have varied substantially during Earth's history, and these variations have driven substantial climate changes at a wide range of timescales




Relative Contributions Of Greenhouse Gases In The Atmosphere From Nine Download Scientific Diagram




Greenhouse Gas Emissions Wikipedia
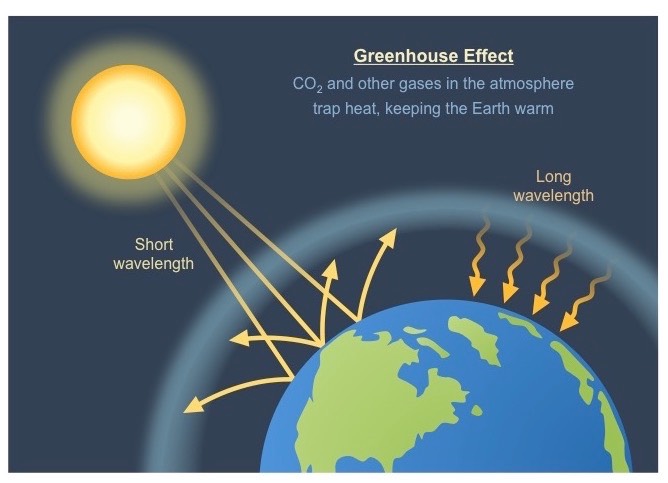
Greenhouse gases are gases—like carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane, and nitrous oxide—that keep the Earth warmer than it would be without them The reason they warm the Earth has to do with the way energy enters and leaves our atmosphere When energy from the sun first reaches us, it does so mainly as lightCarbon dioxide is the main longlived greenhouse gas in the atmosphere Concentrations reached 4055 ppm in 17, 146% of the preindustrial era (before 1750) The increase inGreenhouse Gases and Temperature A greenhouse gas (GHG) is any gas in the atmosphere that absorbs and emits radiation in the thermal infrared range These are the fundamental cause of the greenhouse effect, which results in increased temperatures on Earth The greenhouse effect occurs as the gases reach Earth's surface




Causes Facts Climate Change Vital Signs Of The Planet




Greenhouse Gases Causes Sources And Environmental Effects Live Science
The WMO Greenhouse Gas Bulletin reports on atmospheric concentrations of greenhouse gases Emissions represent what goes into the atmosphere Concentrations represent what remains in the atmosphere after the complex system of interactions between the atmosphere, biosphere, lithosphere, cryosphere and the oceans About a quarter of the totalOf several greenhouse gases, i e , carbon dioxide (CO2) methane (CH4), chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), nitrous oxide (N2O), and tropospheric ozone (O3), have been increasing primarily due to human activities Several ol these gieenhouse gases have long atmospheric lifetimes, decades to centuries, which means that their atmospheric concentrations respond slowly to changes inAs greenhouse gas emissions from human activities increase, they build up in the atmosphere and warm the climate, leading to many other changes around the world—in the atmosphere, on land, and in the oceans The indicators in other chapters of this report illustrate many of these changes, which have both positive and negative effects on people, society, and the environment—including plants and animals Because many of the major greenhouse gases stay in the atmosphere




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa




Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia
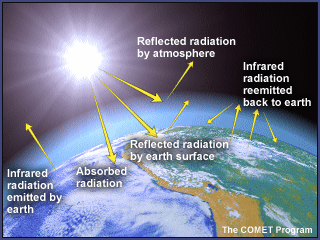
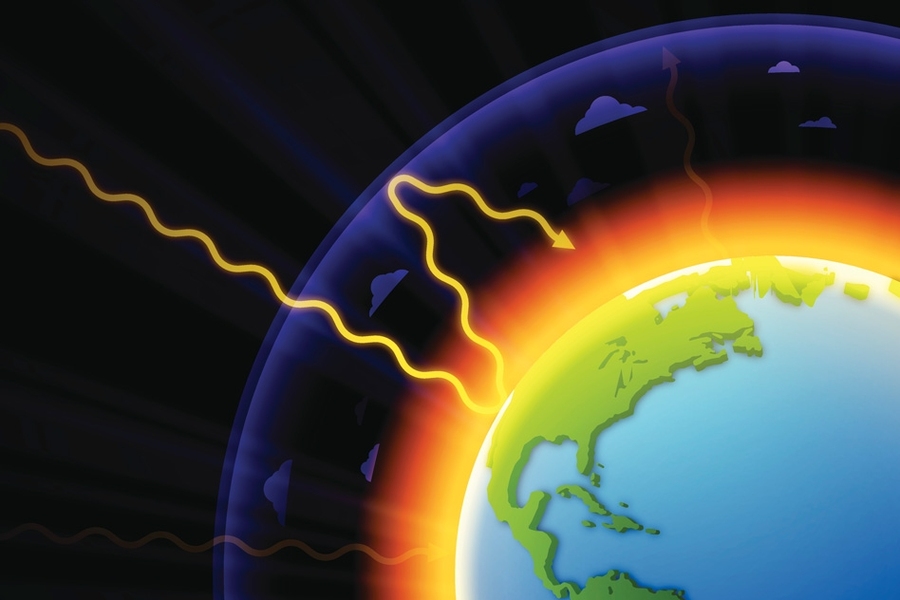
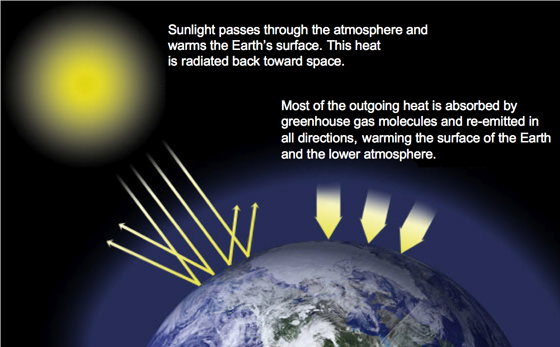
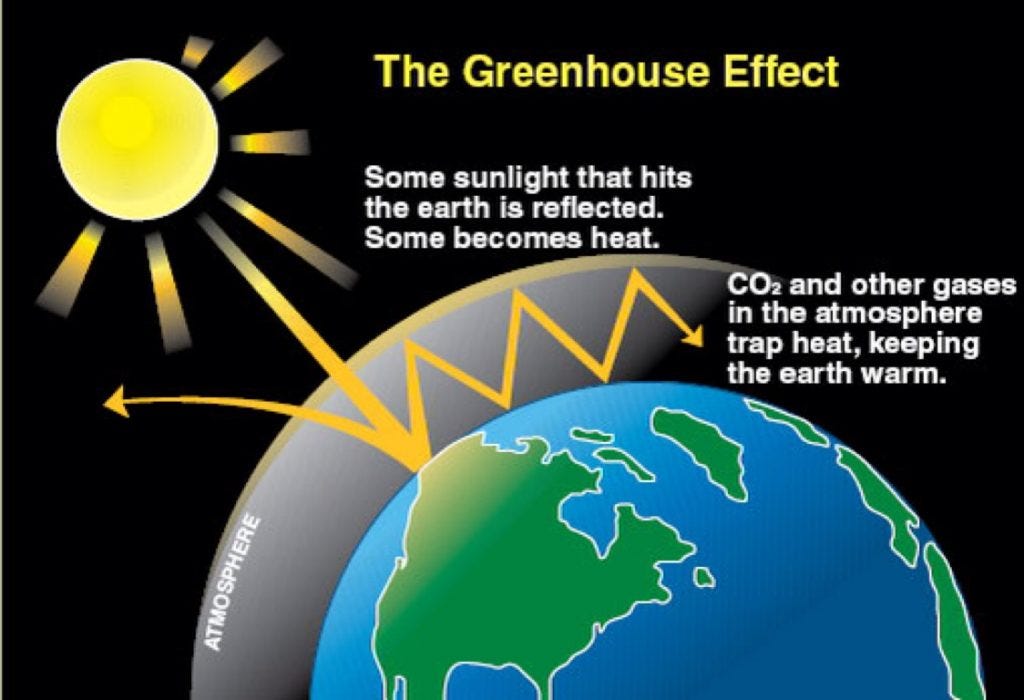
The diagram outlines how the greenhouse effect works Sunlight passes through the Earth's atmosphere The ground warms up and heat is emitted from the Earth's surface Some heat escapes into space What Are Greenhouse Gases?Greenhouse gases trap heat in the atmosphere, in a process called the "greenhouse effect" 1 But how do these molecules actually warm our planet?




Greenhouse Gases Are Rapidly Changing The Atmosphere Climate Central




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Climate Kids
Like other gases in the atmosphere, including oxygen and nitrogen, greenhouse gases are largely transparent to incoming sunlight Unlike those more abundant gases though, greenhouse gases are not transparent to heat (longwave infrared radiation) The sunwarmed surface of Earth radiates heat day and nightGreenhouse gases Sources As greenhouse gases are essential for the existence of life, they are present in the atmosphere in a trace amount Natural sources of GHGs are volcanos, respiration by living organisms, decay and combustion of organic matter, etc The amounts of GHGs are balanced in the atmosphere naturally by many physical, chemicalData for the past 00 years show that the atmospheric concentrations of CO 2, CH 4, and N 2 O – three important longlived greenhouse gases – have increased substantially since about 1750 Rates of increase in levels of these gases are dramatic CO 2, for instance, never increased more than 30 ppm during any previous 1,000year period in this record but has already risen by 30



Greenhouse Gases




Greenhouse Gases Factsheet Center For Sustainable Systems
Overview of Greenhouse Gases Carbon dioxide (CO2) Carbon dioxide enters the atmosphere through burning fossil fuels (coal, natural gas, and oil), Methane (CH4) Methane is emitted during the production and transport of coal, natural gas, and oil Methane emissions Nitrous oxide (N2O) Nitrous The 'greenhouse effect' is the warming of climate that results when the atmosphere traps heat radiating from Earth toward space Certain gases in the atmosphere resemble glass in a greenhouse, allowing sunlight to pass into the 'greenhouse,' but blocking Earth's heat from escaping into space The gases that contribute to the greenhouse effect include water vapor,Let's describe the greenhouse effect The principal gases, yeah In the atmosphere or oxygen and nitrogen these gases are transparent to visible light Mhm From the sun And when this light Mhm Mhm reaches the surface of the earth Mhm Mhm Mhm It is absorbed and converted to heat Yeah Yeah This heat causes atoms in the Earth's surface




What Are Greenhouse Gases David Suzuki Foundation




Climate Change Actual Report Greenhouse Gas Emissions Need For Changing
The greenhouse effect happens when certain gases, which are known as greenhouse gases, accumulate in Earth's atmosphere Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane (CH 4), nitrous oxide (N 2 O), ozone (O 3), and fluorinated gases242 Atmospheric Chemistry and Greenhouse Gases Model calculations of the abundances of the primary greenhouse gases by year 2100 vary considerably across the SRES scenarios in general A1B, A1T, and B1 have the smallest increases of emissions and burdens;The greenhouse effect that has maintained the Earth's temperature at a level warm enough for human civilization to develop over the past several millennia is controlled by noncondensable gases, mainly carbon dioxide, CO 2, with smaller contributions from methane, CH 4, nitrous oxide, N 2 O, and ozone, O 3 Since the middle of the th century, small amounts of manmade gases,




Condition For Greenhouse Gases In The Atmosphere Greenhouse Gases Download Scientific Diagram




Greenhouse Gases American Chemical Society
Greenhouse gases are any gas that goes up into the atmosphere and causes the atmosphere to become warmer by retaining heat from the Sun There's many greenhouse gases Carbon dioxide – we really care about that because it stays in the atmosphere for thousands of years, and so any emissions that we put up there now will be up there for generations to come Aside from water vapour, the four principal greenhouse gases are carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O) and the halocarbons or CFCs (gases containing fluorine, chlorine and



Climate Change Indicators Atmospheric Concentrations Of Greenhouse Gases Climate Change Indicators In The United States Us Epa



Greenhouse Gas Basics 148 Msu Extension



Q Tbn And9gcrevtfvebbghz5zkkbq1akjhfs4 Gwdrbwpqnmfiixo2oqlgyw8 Usqp Cau



Untitled Document




4 Atmospheric Concentrations Of Important Long Lived Greenhouse Gases Download Scientific Diagram



Atmosphere Greenhouse Gases Athenas




The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Space Place Nasa Science For Kids




The Greenhouse Effect British Geological Survey




Air Pollution Greenhouse Gases Britannica
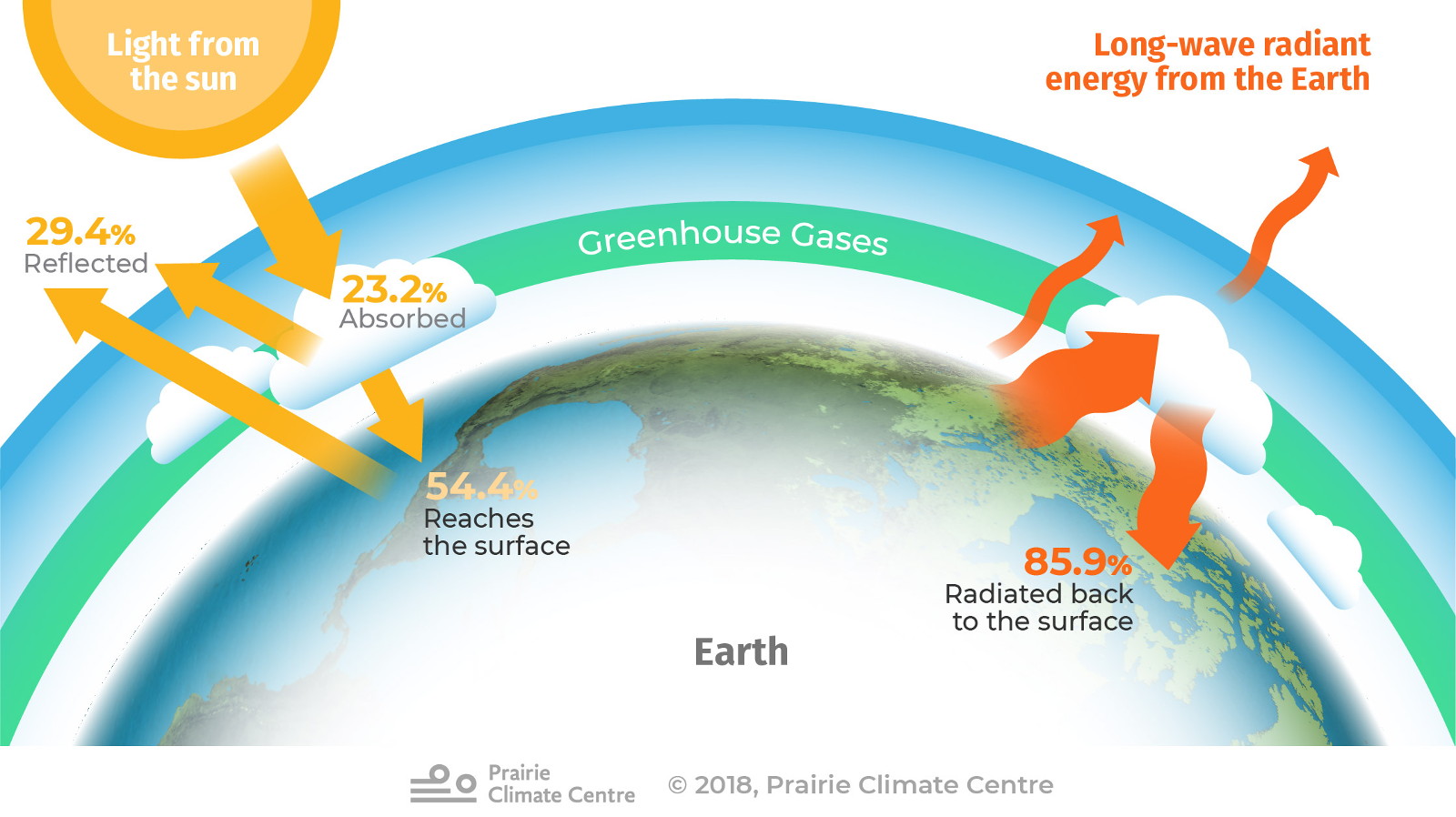



Greenhouse Gases Climate Atlas Of Canada




The Greenhouse Effect Explained




5 Notorious Greenhouse Gases Britannica




Location Location Location Detecting Greenhouse Gas Emissions In Africa Icos




Percentage Of Greenhouse Gases In The Atmosphere Download Scientific Diagram



The State And The Variations Of Greenhouse Gases In The Atmosphere




Greenhouse Gases In Atmosphere Greenhouse Gases Favorite Questions Global




15 Sources Of Greenhouse Gases
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/521928855-58b5c1875f9b586046c8ee0e.jpg)



Worst Greenhouse Gases In The Atmosphere




Greenhouse Effect Definition Diagram Causes Facts Britannica



Ozone



Greenhouse Gases




Greenhouse Gases In Atmosphere Hit New High Un Egypt Independent



3



Greenhouse Gases Effect On The Climate And Climate Change




Indicator Annual Greenhouse Gas Index 18 Indicator Annual Greenhouse Gas Index Gcis



Q Tbn And9gcs3 Vn3xnwnq9ifctpyrsa2ofh2ymxfw2rxlcy7frr77uflqr Usqp Cau




Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia
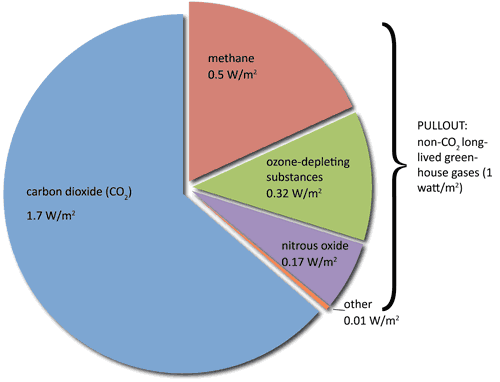



Greenhouse Gas It S Not Just About Co2




What Are Greenhouse Gases Answered Twinkl Teaching Wiki




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc




Carbon Dioxide Methane Nitrous Oxide And The Greenhouse Effect Conservation In A Changing Climate



Q Tbn And9gcqob5akx 2xithdb3seiv5jyef5ryrbg3xvzguy4p57lypo5m0p Usqp Cau




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa




Greenhouse Gas Concentrations Surge To New Record World Meteorological Organization




The Science Hoosier Environmental Council



Atmospheric Greenhouse Gas Concentrations European Environment Agency



Atmospheric Greenhouse Gas Concentrations European Environment Agency




The Greenhouse Effect
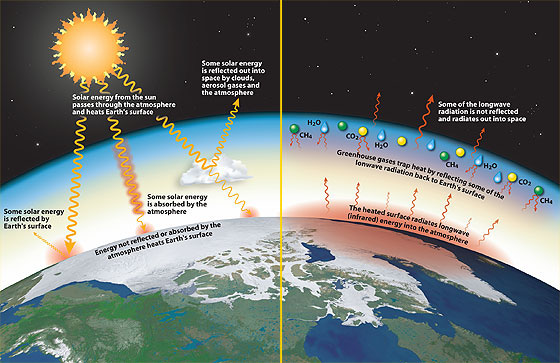



Too Much Of A Good Thing




Greenhouse Gases Bioninja
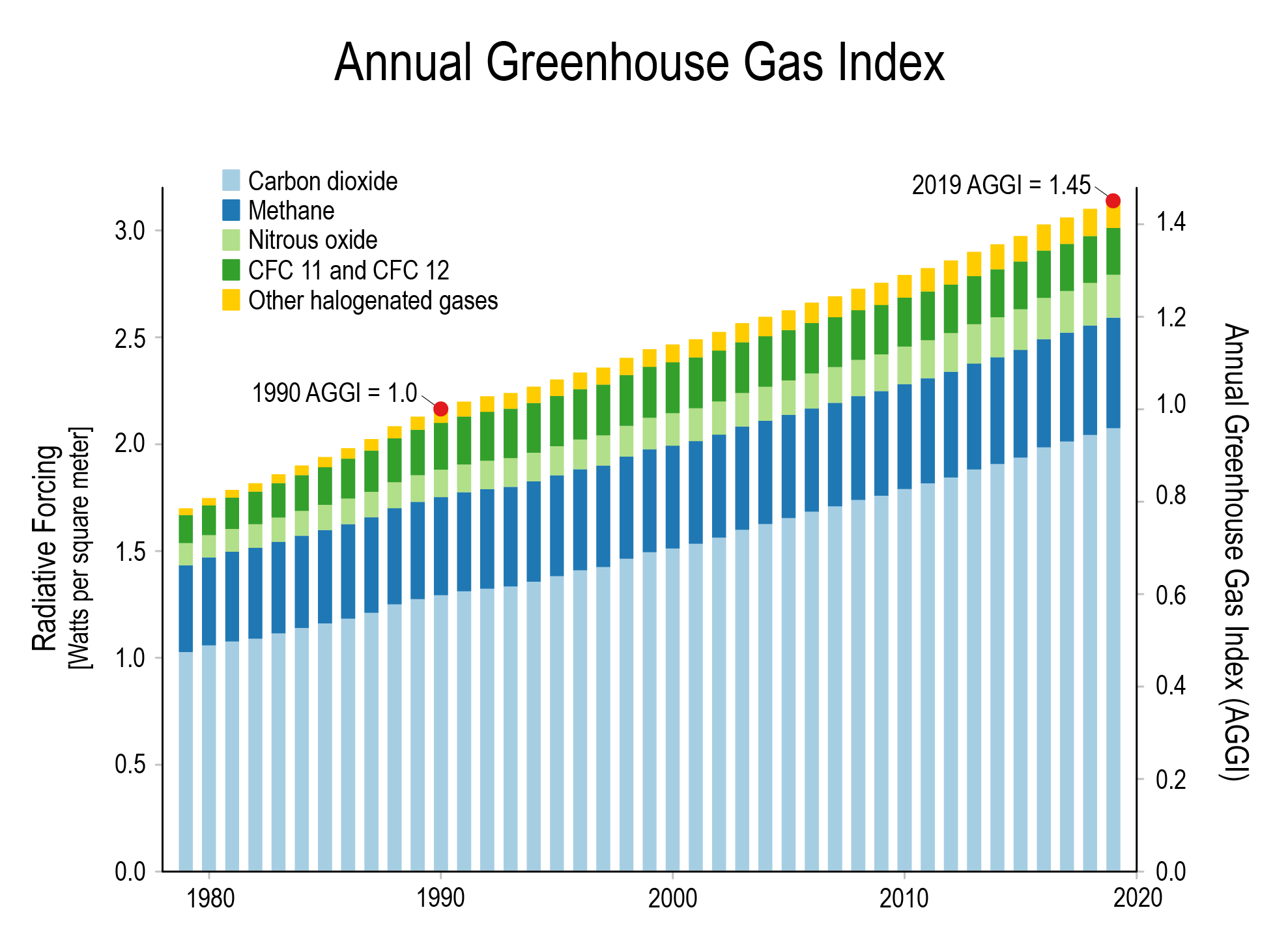



Climate Change International Ccs Knowledge Centre
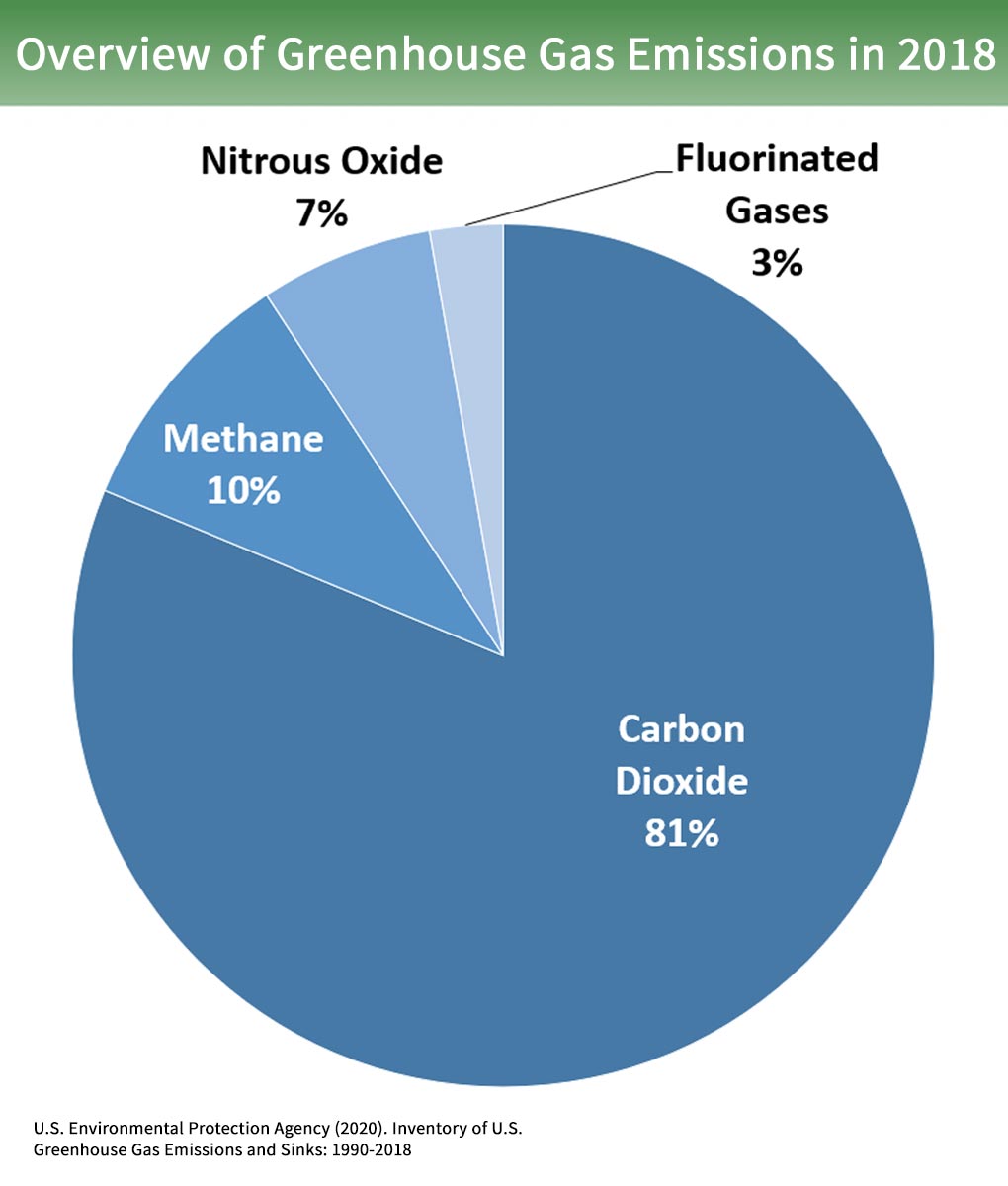



Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Greenhouse Gas Ghg Emissions Us Epa
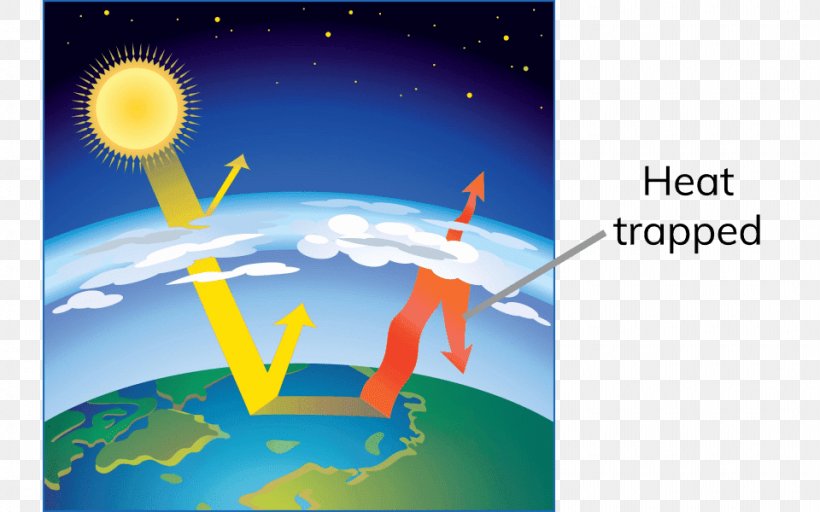



Earth Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gas Atmosphere Png 960x600px Earth Atmosphere Atmosphere Of Earth Brand Climate Download




Greenhouse Gas Concentrations In Atmosphere Reach Yet Another High World Meteorological Organization
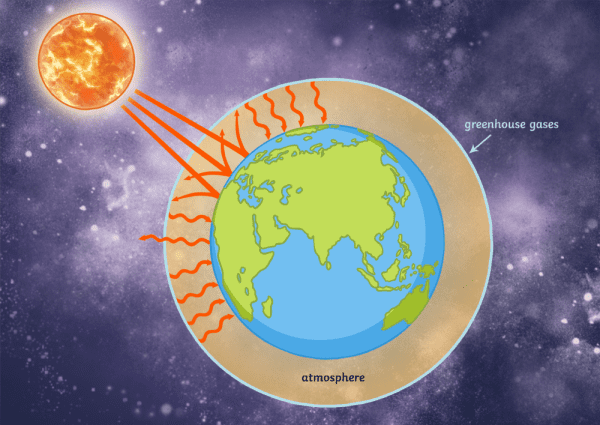



What Are Greenhouse Gases Answered Twinkl Teaching Wiki
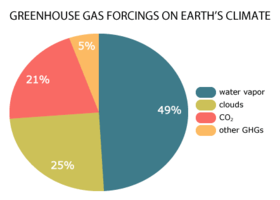



Which Are The Most Common Greenhouse Gases In The Atmosphere Socratic




Greenhouse Gases Copernicus




Carbon Dioxide In The Atmosphere Is At A Record High Here S What You Need To Know



Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia




Wmo Greenhouse Gas Bulletin The State Of Greenhouse Gases In The Atmosphere Based On Global Observations Through 18 No 15 25 November 19 World Reliefweb




Atmospheric Concentrations Of The Three Main Greenhouse Gases Carbon Download Scientific Diagram



Climate Science Investigations South Florida Energy The Driver Of Climate




Greenhouse Gases Copernicus
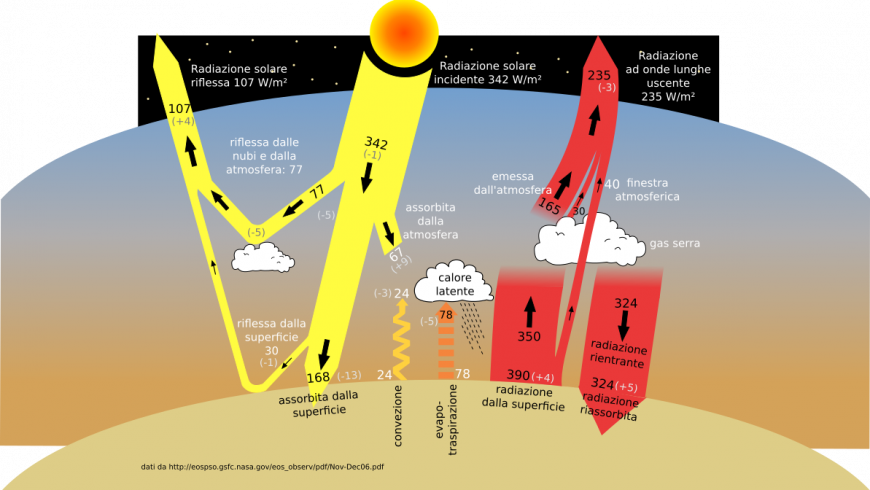



Greenhouse Gases What Are They What Can We Do To Reduce Emissions




Percentage Share Of Greenhouse Gases In The Earth Atmosphere 5 Download Scientific Diagram




Banning The Super Greenhouse Gas Environment All Topics From Climate Change To Conservation Dw 17 10 16
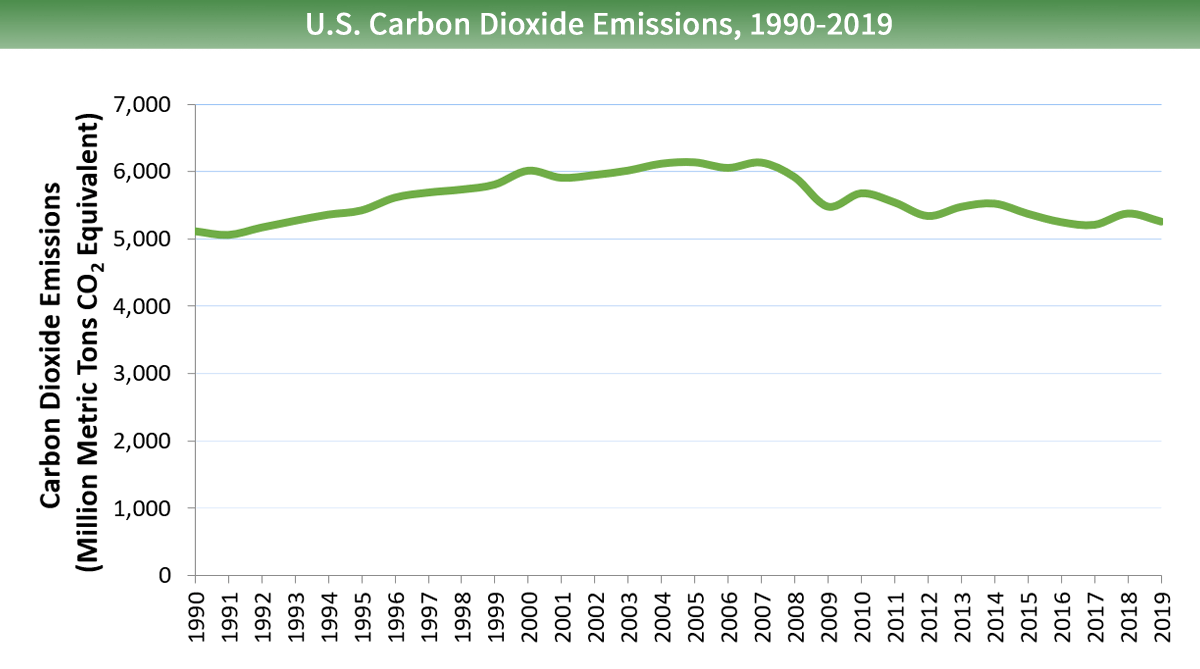



Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa
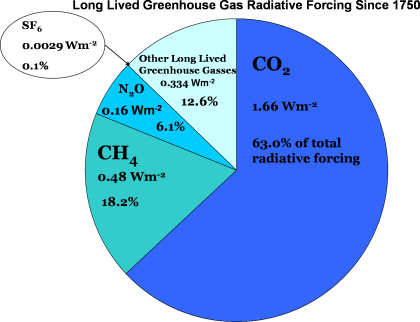



Noaa Esrl Global Monitoring Laboratory




Greenhouse Gases Are Components Of The Atmosphere That Contribute To The Greenhouse Effect




World Greenhouse Gas Levels Made Unprecedented Leap In 16



Greenhouse Gas Global Greenhouse Warming




Greenhouse Gases Edexcel Igcse Biology Revision Notes




Greenhouse Gas Levels In Atmosphere Reach New Record United Nations Sustainable Development
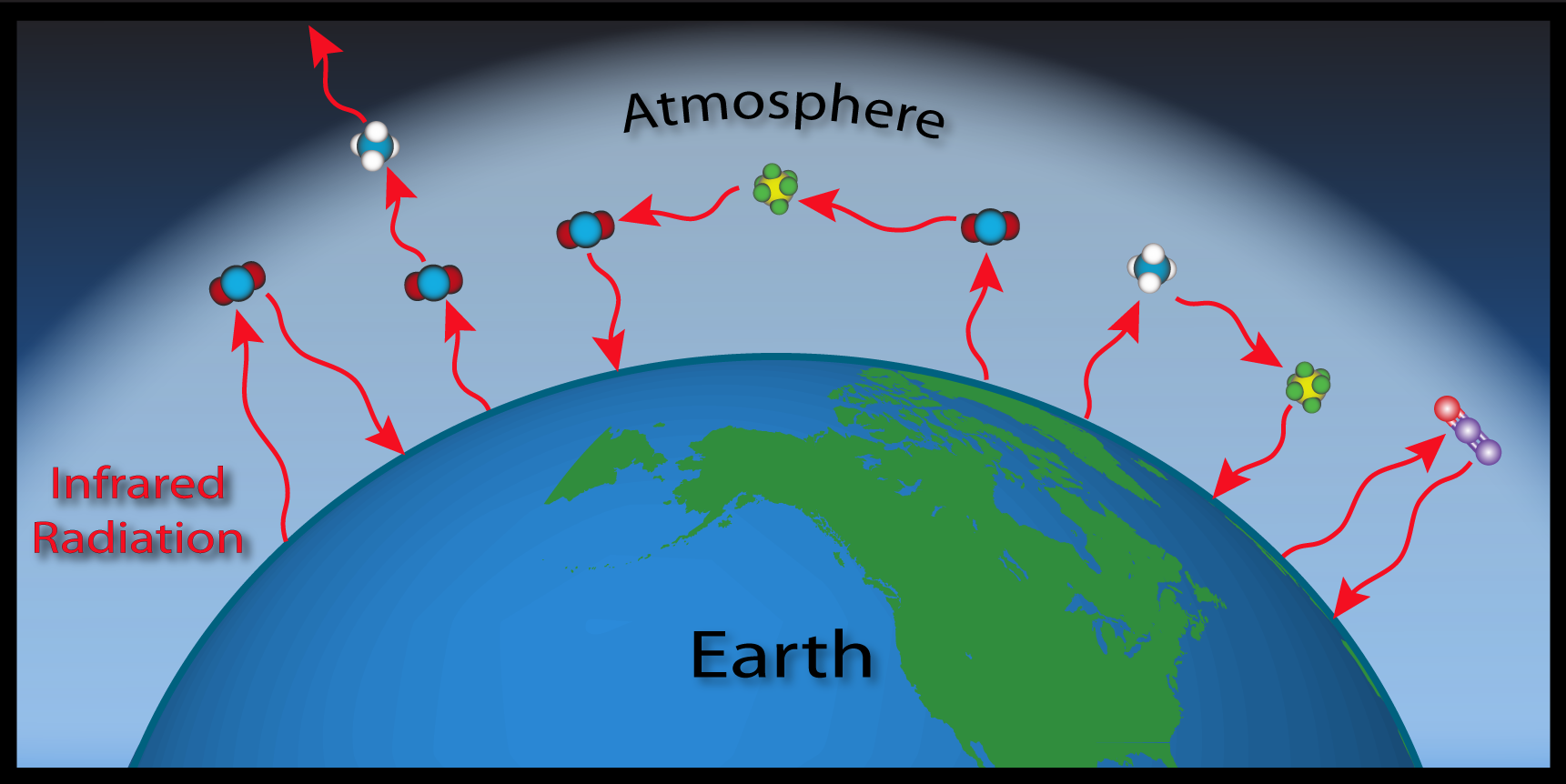



Esrl Global Monitoring Laboratory Education And Outreach



Atmospheric Greenhouse Gas Concentrations European Environment Agency



Greenhouse Gases Climate Aware



Climate Science Investigations South Florida Energy The Driver Of Climate



How Do Greenhouse Gases Trap Heat Socratic



Atmo336 Fall




Climate Change Atmospheric Carbon Dioxide Noaa Climate Gov



Greenhouse Gases




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa



Greenhouse Effect Advantages And Disadvantages By Tutorbin Medium



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿